Mechanisms of bacterial intramacrophage survival and anti-virulence strategies
Head of group: Dr. Anne Blanc-Potard
Our goal is to better understand the intramacrophage phase encountered by the extracellular bacterial pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa, particularly in the context of cystic fibrosis (CF). We have identified various bacterial factors involved in this step, which constitute therapeutic targets for new anti-infective molecules.
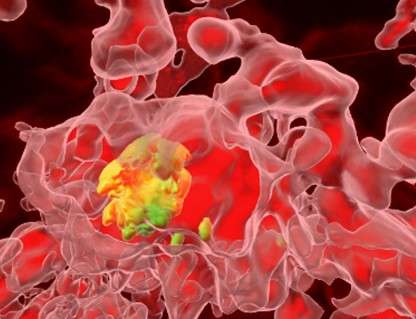
We develop the zebrafish embryo model to define the involvement of this intramacrophage phase in the establishment and persistence of the infection, in a normal or CF context. We are also using this vertebrate model to test new strategies to limit P. aeruginosa infection.